Virtual Reality Simulation-Based Robotic Technician Assessment
Virtual Reality Simulation
Vr training, VR based assessments, Virtual reality manufacturing training, Conversation AI, Job skill assessment
Objective
To demonstrate the potential offered by VR technology for credentialing and training of the robotics workforce.
Overview
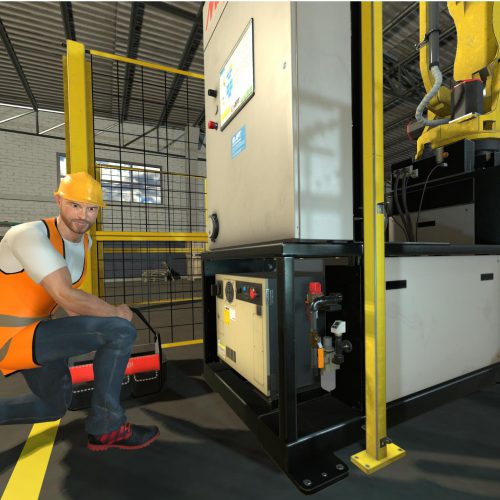
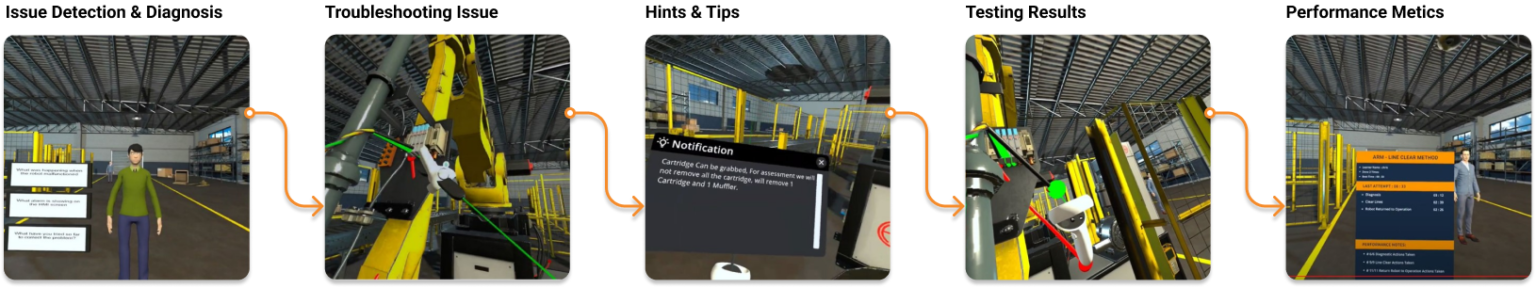
Siminsights partnered with the ARM Institute to develop a VR based robotics technician assessment. The program focuses on analyzing a potential hire’s expertise in handling the maintenance of a palletizing robot in a virtual environment.
The assessment simulation, authored in HyperSkill, presents the user with a fault and asks the user to troubleshoot. SimInsights created a high-fidelity simulation capable of producing observations of users actions in a manner that supports gathering of detailed evidence for assessment of their proficiency on specific standards.

Challenges
- Many experienced technicians do not possess formal training or credentials. This may be a limiting factor for their career progression. Formal training is often avoided because it is prohibitively time consuming and expensive. Therefore it is ideal to have a scalable method of assessment and credentialing.
- In the conventional assessment method (i.e., not VR-based), the subject matter expert (SME) would take a potential hire into the manufacturing environment, with a deactivated work cell, taken out of production. Then providing them with a potential error prompt. This conventional assessment method of taking an expert and a machine out of a field to evaluate a potential hire is
- Costly
- Time consuming
- Limited to few users
- Potentially unsafe
VR Solutions : Create 6 DOF VR immersive manufacturing environment
Siminsights project team worked with Dr. Ayesha Madni, Professor Mark Steyvers, the SMEs and the ARM Institute team to conduct the Cognitive Task Analysis. Analysis Assessment design was based on inputs from SME, Jonathan Clingan, on tasks related to troubleshooting and maintenance for the machine. Once the standards were set, the Scoring Model scheme was implemented. Based on the Scoring Model scheme, Hyperskill allows the user to proceed with the simulation to demonstrate their competency with other steps, even if they may not have completed a preceding step successfully.
Ultimately, when providing feedback to the user on their completion of the entire simulation, Hyperskill indicates which steps and substeps they completed successfully for partial and total scores. It also provides the requisite remediating information. In other words, a user gets feedback about particular content aspects and steps (e.g., safety procedures) where they may require additional practice, or where they have achieved adequate competence.
AI methods were used to implement conversational capabilities. Users can give voice commands to virtual humans in the simulation to obtain information. Users’ voice commands are logged and can be used in the assessment.
Delivery
SimInsights’ primary deliverable was a high fidelity simulation of a virtual reality manufacturing training environment. This environment contained highly realistic graphics and interactions, capable of producing observations of users’ knowledge, skills and abilities (KSA). Such information is used to gather evidence for valid and reliable assessment for certification and credentialing.
A tutorial was created and iteratively refined with pilot testing feedback. Another highlight of the simulation was the inclusion of conversational artificial intelligence (AI) to simulate dialogue between the worker and two virtual human assistants who played the role of a supervisor and a work cell technician.
Benefits
Credentialing for technicians who have years of experience but have not had recognized/formal training and assessment
- There are many competencies for technicians, so VR work cells are more scalable
- The user would be able to actually perform the tasks rather than verbally describe what actions they would do.
- The company conducting the assessment would not need to take an otherwise functioning robot out of the production line to conduct the assessment.
- A subject matter expert (SME) is not required to assess the performance of every user.
